The Warehouse Inspections module is used to document and control stock inspections within a warehouse. Each inspection record stores the issuing company, the inspected warehouse, the responsible employee and the reason for the inspection.
Below is an overview of the interface layout, followed by a detailed explanation of each section and field.
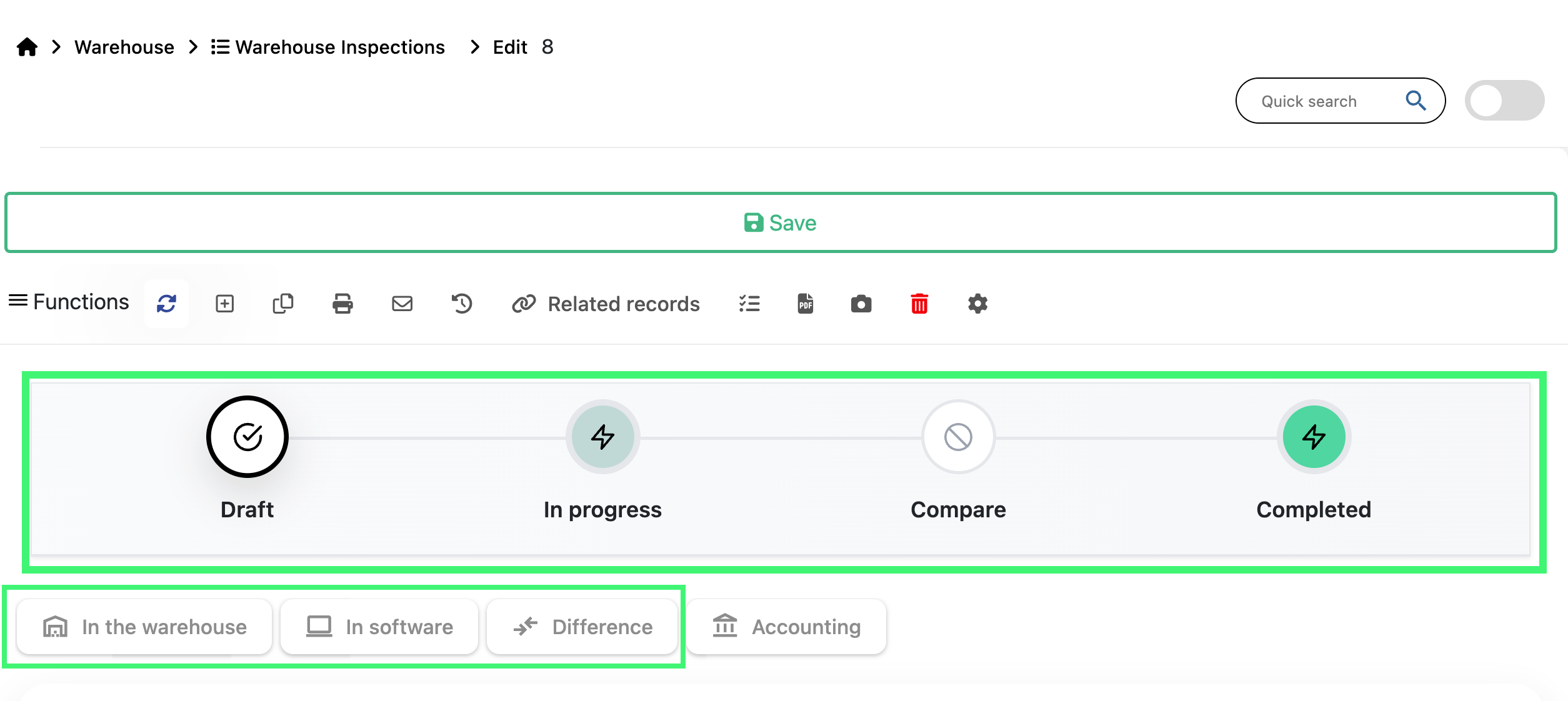
Inspections Interface
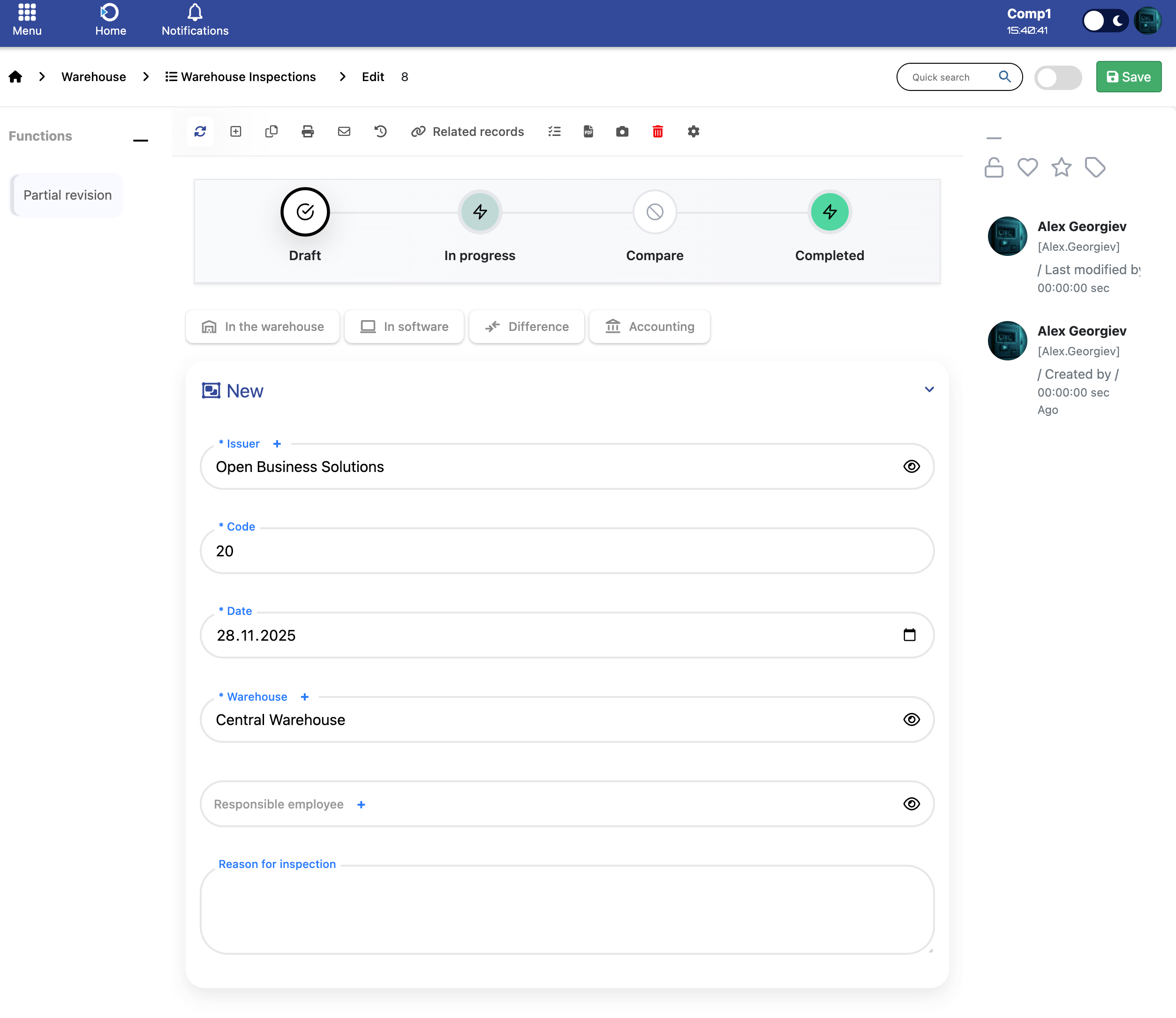
Defines who is creating the inspection document.
- Issuer – The company responsible for initiating the inspection.
Indicates which warehouse is being inspected.
- Warehouse – The warehouse where the inspection is carried out.
Core information that uniquely identifies and describes the inspection.
- Code – Unique inspection number.
- Date – The date the inspection is created or performed.
- Responsible employee – Employee performing or supervising the inspection.
- Reason for inspection – Explanation for the inspection (e.g. periodic check, discrepancy, maintenance).
Scope tabs help focus on different aspects of the inspection:
- In the warehouse – Physical counted quantities.
- In software – Quantities recorded in the ERP system.
- Difference – Shows discrepancies between physical and system values.
- Accounting – Information for accounting adjustments.
Quick actions available for the inspection document.
- Partial revision – Start a partial inspection.
- Related records – View linked documents.
- Save – Saves the inspection document.
The workflow tabs displayed at the top of the inspection document help the user complete the inspection step by step. Each tab provides a different view of the inspection data:
- In the warehouse – Used to manually enter the physically counted products and quantities available in the store or warehouse during the inspection.
- In software – Displays the system quantities pulled automatically when the inspection enters the In progress state. No manual input is required here.
- Difference – Shows the comparison between the physical count (“In the warehouse”) and the system count (“In software”). Any shortages, surpluses, or mismatches become visible here. The difference view becomes active when the inspection is moved to the Compare stage in the workflow.